New WHO Initiative Boosts Hospital Preparedness Across Egypt
WHO Egypt started a national training program to improve the ability of hospital units across the country to respond to emergencies. Standardizing medical operational procedures is the main goal of the program, which is to make people more ready for mass casualty events. The UK government gave money to help make emergency healthcare more resilient in institutions.
The initiative brings together regional and country offices at the headquarters level to coordinate technical advice and operational implementation across the country. Health officials stressed the need to improve long-term crisis response infrastructure planning while also making sure that frontline workers are ready for anything. The program directly helps Egypt’s national health emergency preparedness plan in many cities.

Source: WHO/Website
Programme Certifies Instructors To Expand Emergency Response Expertise Nationwide
16 national instructors successfully completed certification under the new training of trainers medical preparedness programme. These teachers were quickly sent to major hospitals to lead structured emergency management training sessions. During the first phase of the program’s implementation, 60 healthcare professionals from Cairo and Ismailia took part.
The people who took part were from emergency departments, trauma units, and hospital administration teams that were in charge of coordinating disaster response. The training stressed the need for standardized procedures for assessing casualties, setting priorities for triage, and setting up communication systems for operations. Graduates will be in charge of training people at institutions for future regional capacity building projects.
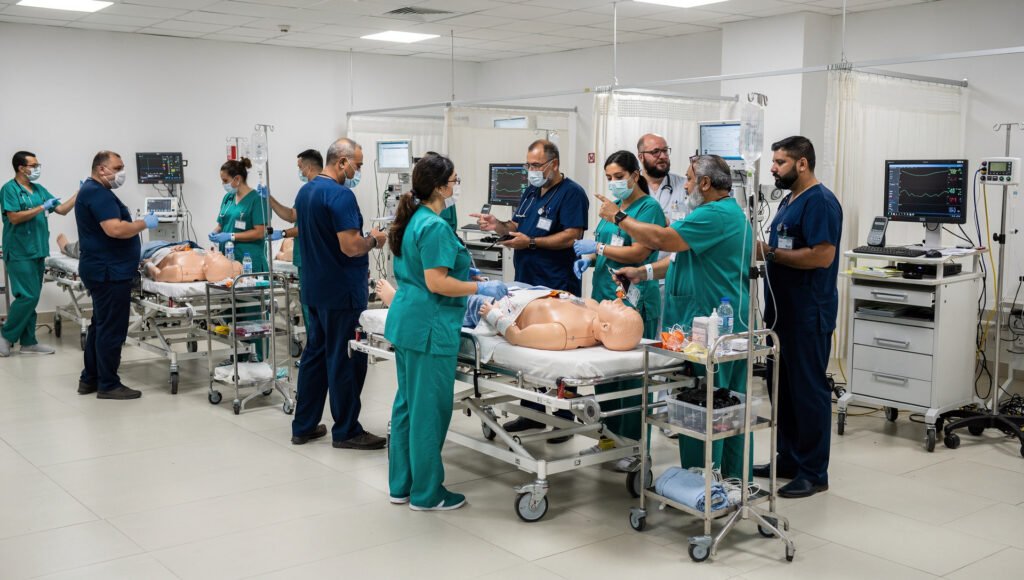
Blended Learning Model Combines Digital Modules With In Person Simulations
The program uses a blended learning model that combines online lessons with hands on exercises in a hospital. The WHO Academy platform was used to deliver digital modules for standardized learning. Later, the participants went to structured workshops where they learned about practical emergency management skills.
Trainees were able to practice triage classification, treatment coordination, and emergency logistics planning procedures in hands on sessions. Simulation scenarios imitated authentic hospital congestion circumstances during mass casualty events. Facilitators used standardized assessment frameworks to see how well participants did.
Recommended Article: OneAdvanced Acquires Patchs Health to Expand AI Platform
Curriculum Focuses On Hospital Triage Organization And Treatment Coordination
The training modules taught important ideas about how hospitals should prepare for disasters and how to set up structured plans for responding to emergencies. Participants learned how to set up treatment areas based on how sick the patients were and what resources were available. During large scale medical emergencies, it was important to keep treatment delays to a minimum.
The program explained how responders should talk to each other, what their roles should be, and how to get things going in an emergency. To help people make decisions in busy clinical settings, action cards and procedural checklists were added. These tools are meant to make outcomes more consistent, accurate, and likely to save patients lives.
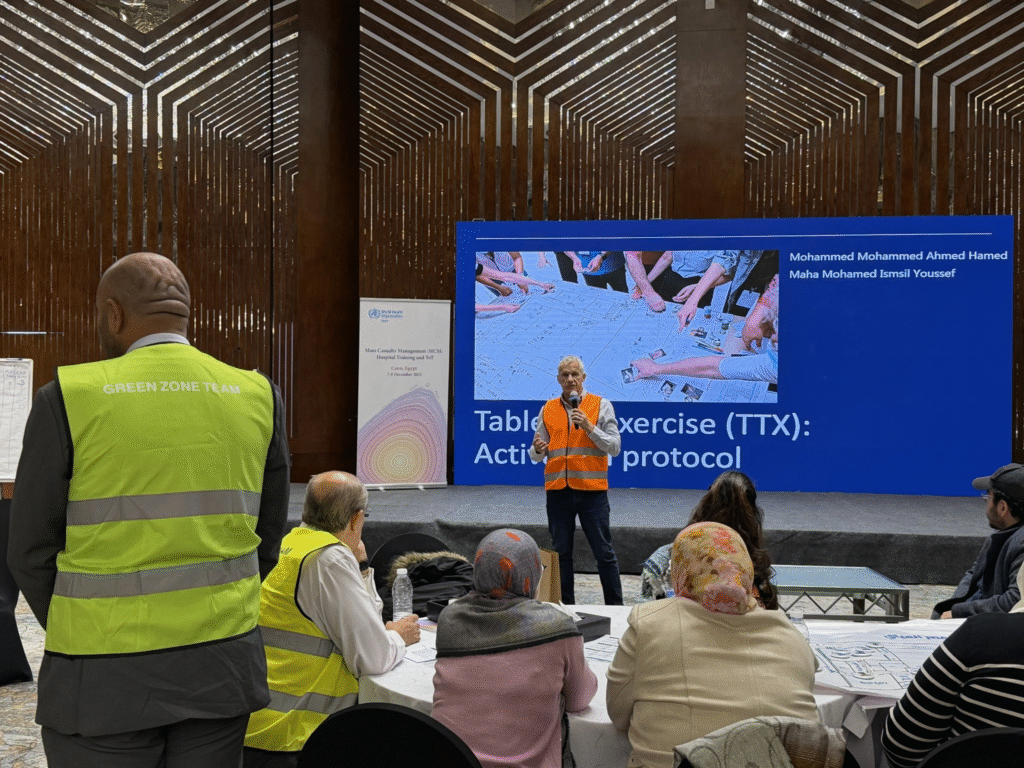
Tabletop Exercises Refine Real World Hospital Emergency Response Planning
Participants did tabletop simulations that were like real life mass casualty situations that happened in urban healthcare facilities. Teams looked over emergency workflows and found problems with their institutional response frameworks. Facilitators led structured evaluations of how resources were used and how patients were moved around.
Hospitals improved their emergency plans based on the operational gaps that were found during the practice drills. Teams gave presentations on staffing shortages, problems with distributing equipment, and problems with coordinating between departments. Feedback sessions focused on how structured preparedness planning cycles can help people get better all the time.
WHO Partnership Strengthens Long Term Resilience Of Egyptian Health System
WHO officials stressed how important the program is for building up the country’s long term emergency healthcare capacity. One of the long term goals is to make emergency preparedness training a regular part of hospital staff development programs. The project fits in with larger plans to lower the risk of disasters in the region.
Strengthening national networks of instructors makes it possible for healthcare institutions all over the country to share knowledge in a way that can be scaled up. Officials think that this method will make sure that training continues after the first program implementation cycles. The model helps people stay strong in the face of natural disasters, accidents, and public health emergencies.
Egypt Expands Emergency Readiness Through International Health Cooperation Efforts
Egypt’s plan to improve its healthcare emergency preparedness still relies heavily on working with other countries. The UK helped strengthen investments in technical infrastructure and training. WHO’s regional coordination made sure that everything was in line with global emergency response standards.
Health officials expect to roll out similar programs in more governorates in the next few years. By sending instructors out all the time, training will keep going at all of the regional medical centers. Officials see the program as a building block for being ready to handle future national crises.